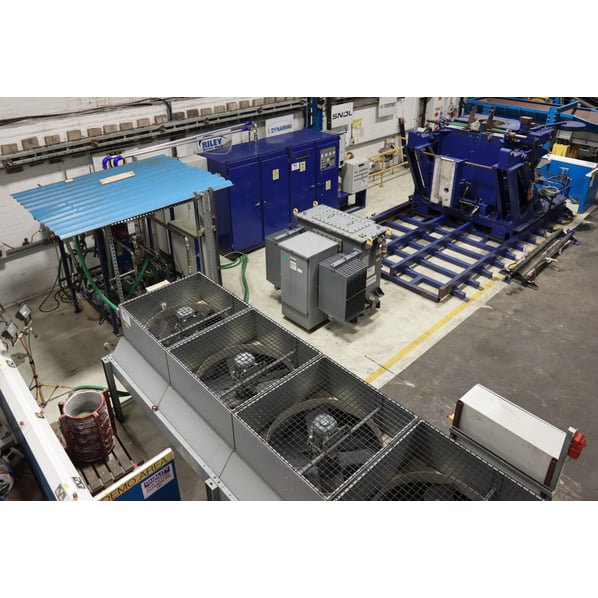
Induction Heating Systems Limited Induction Melting Furnace


- Stock No
- OC2497S
- Manufacturer
- Induction Heating Systems Limited
- Model
- 1 Tonne Tipping Melting Furnace
- Year of Manufacture
- 2016
- Serial
- C533
- Condition
- Excellent Condition, Ex demonstration, Seen powered at RSW
- Internal Size (WxDxH mm) [?]
- Ø 600 x 1050 mm
- Max Temp
- Metal Dependent
- Other Info
- Frequency 250-1000Hz, 500KW
- Location
- Our Central Warehouse, Aldridge, UK
- Weight (kgs)
- 2641
- External Dimensions (WxDxH mm) [?]
- Ø 2450 x 3000 (2200 without Platform)
- Delivery Your delivery options
Description
Induction Heating Systems Induction Melting Furnace
An induction furnace is an electrical furnace in which the heat is applied by induction heating of metal. Induction furnace capacities range from less than one kilogram to one hundred tons, and are used to melt Iron and Steel, Copper, Aluminium and precious metals.
In the induction furnace, a coil carrying alternating electric current surrounds the container or chamber of metal. Eddy currents are induced in the metal (charge), the circulation of these currents producing extremely high temperatures for melting the metals and for making alloys of exact composition.
Specialty steelmaking shops and foundries, induction furnaces are cylindrical, open-topped, tiltable refractory crucibles with a water-cooled induction coil installed on the outside, around the side wall. The coil is powered by alternating current, which induces eddy currents in the metallic charge that generate heat. The refractory wall of the crucible.
Input Rating
- Power: 585 (kVa)
- Phases: 3
- Voltage: 415 (v)
- Current: 814 (a)
- Frequency: 50 (Hz)
Output Rating
- Power: 500 (kW)
- Voltage: 2000 (volts)
- Current: 993 (A)
- Frequency 250 min - 1000 max (Hz)
Technical Overview
The advantage of the induction furnace is a clean, energy-efficient and well-controlled melting process, compared to most other means of metal melting.
Most modern Foundries use this type of furnace, and many iron foundries are replacing Cupola Furnaces with induction furnaces to melt Cast iron as the former emit much dust and other pollutants.
Induction furnaces do not require an arc, as in an electric arc furnace, or combustion, as in a Blast Furnace. As a result, the temperature of the charge (the material entered into the furnace for heating, not to be confused with electric charge) is no higher than required to melt it; this can prevent the loss of valuable alloying elements.
The one major drawback to induction furnace usage in a foundry is the lack of refining capacity: charge materials must be free of oxides and be of a known composition, and some alloying elements may be lost due to oxidation, so they must be re-added to the melt.
Operation
An induction furnace consists of a nonconductive crucible holding the charge of metal to be melted, surrounded by a coil of copper wire. A powerful alternating current flows through the wire. The coil creates a rapidly reversing magnetic field that penetrates the metal. The magnetic field induces eddy currents, circular electric currents, inside the metal, by electromagnetic induction. The eddy currents, flowing through the electrical resistance of the bulk metal, heat it by Joule heating. In ferromagnetic materials like Iron, the material may also be heated by magnetic hysteresis the reversal of the molecular magnetic dipoles in the metal. Once melted, the eddy currents cause vigorous stirring of the melt, assuring good mixing.
An advantage of induction heating is that the heat is generated within the furnace's charge itself rather than applied by a burning fuel or other external heat source, which can be important in applications where contamination is an issue.
Operating frequencies range from utility frequency (50 or 60 Hz) to 400 kHz or higher, usually depending on the material being melted, the capacity (volume) of the furnace and the melting speed required. Generally, the smaller the volume of the melts, the higher the frequency of the furnace used; this is due to the skin depth which is a measure of the distance an alternating current can penetrate beneath the surface of a conductor. For the same conductivity, the higher frequencies have a shallow skin depth—that is less penetration into the melt. Lower frequencies can generate stirring or turbulence in the metal.
A preheated, one-ton furnace melting iron can melt cold charge to tapping readiness within an hour. Power supplies range from 10 kW to 42 MW, with melt sizes of 20 kg to 65 tons of metal respectively
Advertised in partnership with Induction Melting Repairs Limited https://www.imr-ltd.co.uk/

Representatives of Induction Melting Repairs Limited have been involved in the professional decommission of the Induction Melting furnace, they have tested for complete functionality and can provide professional installation, ongoing service and spare and supports.
Option to Include: Transformer, Air Blast Cooler, Spare Unused Furnace Body & Induction Coil
Thermal Transfer Technology Air Blast Cooler
3T’s ranges of Dry Air Liquid Coolers are all designed with high energy efficiency in mind. All of their unit components are selected using the best technology currently available. Flatbed (horizontal or vertical) and V-type orientations are available.
Standard Features include:
- Standard high efficiency AC fans or optional EC fans for low energy consumption.
- Tube materials include copper, stainless steel 304 or 316 and titanium.
- Fins available in aluminium, coated aluminium, copper, copper tinned, aluminium magnesium,
stainless steel 304 or 316 and titanium. - Casework in plain galvanised steel, powder coated galvanised steel, stainless steel 304 or 316 and brass.
- Individual isolators.
- Step control.
- Inverter control.
- Common terminal box.
- Adiabatic system available for extra capacity in high ambient temperature conditions.
Actual Technical details of the Thermal Transfer Technology Air Blast Cooler (see separate full description)
Model: SSL-S-144-65-900H-3 x 400 -50Hz
Serial no: 32400/1.1
YOM: 2016
Min/max limit: -1/11.5 Bar (G)
Test Pressure: 15 Bar (G)
Fluid Water/Ethylene Glycol: 25% Volume
Internal volume: 75 Litres
Weight (dry): 971kg
Motor Data
Motors: 4 off
Supply: 4 x 400 volt - 50Hz
Rated Power: 2.2kW Fan
Full Load Current: 6.4 Amps
Fan Speed: 900 rpm
Bowers Transformer (see separate full description)
- Sizes: 1750 x 1950 x 1900mm
- Output: 600kVA
- Voltage Ratio: 11000/400
- Amperes: 31.49/866.0
- Phases: 3
- Frequency: 50Hz
- Total weight: 2950Kg's
Approximate Dimensions
Induction Furnace
2450 x 3000 (2200 without Platform) x 2500mm Internal (Working Melting Chamber)– Ø 600 x 1050 mm
Bowers Transformer – 1750 x 1950 x 1900mm
Air blast cooler - Pump, CP & Pipe Housing - 2240 x 1570 x 1720mm
Air blast cooler - 4550 x 1670 x 1700mm
![]() Print / Download Induction Heating Systems Limited Induction Melting Furnace Datasheet
Print / Download Induction Heating Systems Limited Induction Melting Furnace Datasheet
Additional files
Photographs taken prior refurbishment. Our refurbishment service is not available on all machines.
Machines & equipment for sale
- Surface Treatment
- Cleaning & Degreasing
- Polishing & Belt Linishing
- Mass Finishing
- Ovens & Furnaces
- Process Cooling
- Shot Blasting
- Dust & Fume Extraction
- Air Compressors
- Rectifiers & Transformers
- Miscellaneous
- Latest Stock
- Special Offers
- Direct From Site Clearances
- Auctions
- Brand New Machines
- Available Immediately
- Sell Your Machine
Machine Alert
Get the latest machines emailed directly to you as they become available to buy online. Sign Up Now